Automotive Relays: What are They and How Do They Work?
Posted on July 29, 2025

That satisfying click when you turn on your headlights? The instant response when you hit the power windows? You can thank automotive relays—your vehicle's silent electrical bodyguards.
These palm-sized components work tirelessly to protect delicate switches from high-current damage, act as traffic cops for your car's electrical flow, and prevent wiring meltdowns by handling heavy loads.
Here's the shocking truth: Without relays, your car's electrical system would be like running a microwave through a lamp cord: dangerous and inefficient.
In this guide, we'll explain:
- How relays work (it's simpler than you think)
- Why does your car have dozens of these hidden helpers
- How to spot failing relays before they strand you
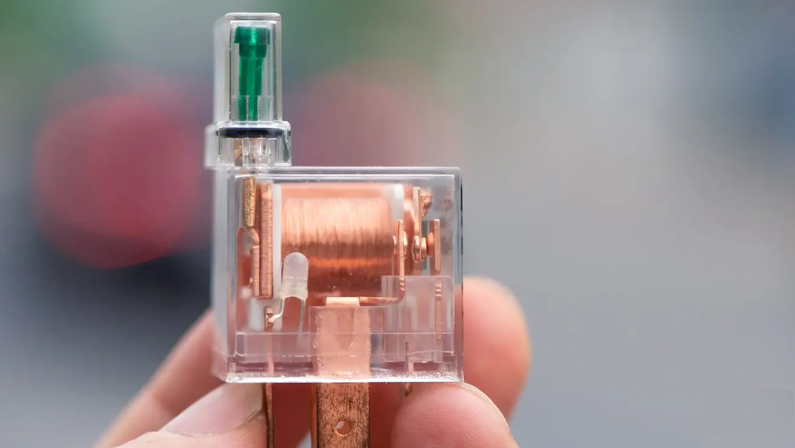
What is a Relay in a Car?
A relay in a car is an electrical switch that helps control the flow of power in your vehicle. It’s designed to work with DC (direct current) voltage, which is what most car systems use.
You’ll find relays used in many parts of the car, from comfort features like power windows and seats to important safety systems like headlights and ignition.
At its core, a car relay uses a small amount of electricity to control a larger electrical current. It works with an electromagnet that activates when a small current passes through it.
This magnet then opens or closes the circuit to let a larger current flow through. In simple terms, relays help your car use low-power signals to safely and efficiently manage high-power functions.

Why are Relays Used in Cars?
Relays play a major role in managing your car’s electrical system. They’re essential for handling high-powered devices, simplifying control, and allowing automation through the car’s computer system. Here’s how they help:
1. Handle High-Power Currents
Many vehicle systems, like the starter motor, cooling fan, and headlights, require a lot of electrical power to run. Relays make it possible to control these powerful systems with smaller, low-power switches inside the cabin.
Instead of running thick, expensive wires from the dashboard to each device, relays are installed close to the high-power components under the hood. This setup reduces wiring complexity and helps save space and money.
2. Help Control Electronics More Conveniently
Thanks to relays, you can use simple buttons and switches on your dashboard to manage powerful systems like the air conditioning or wipers. Without relays, each control inside the cabin would need to be bulky enough to handle high electrical currents directly.
Relays act as middlemen, taking the signal from the small switch and powering the big components, making your driving experience smoother and more user-friendly.
3. Automate Power Distributions
Relays make it easier to automate when and how power is delivered to different parts of your car.
For example, they can be used to automatically turn on your radiator fan when the engine gets too hot or switch off your headlights after the car shuts down. This automation improves efficiency and protects the vehicle from unnecessary strain.
4. Protect Electrical Components
By managing how and when high currents flow, relays help protect sensitive parts of your car’s electrical system.
Instead of exposing your dashboard controls or small wires to large amounts of power, relays take the load and direct the energy safely, which helps prevent overheating or damage to important components.
5. Allow the Computer to Control Vehicle Features
Modern cars are full of automated systems controlled by the vehicle’s computer, known as the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Relays help the PCM control features like the fuel pump, ignition system, and radiator fan without the computer handling high power directly. This allows the vehicle to run smarter, more efficiently, and with better safety.
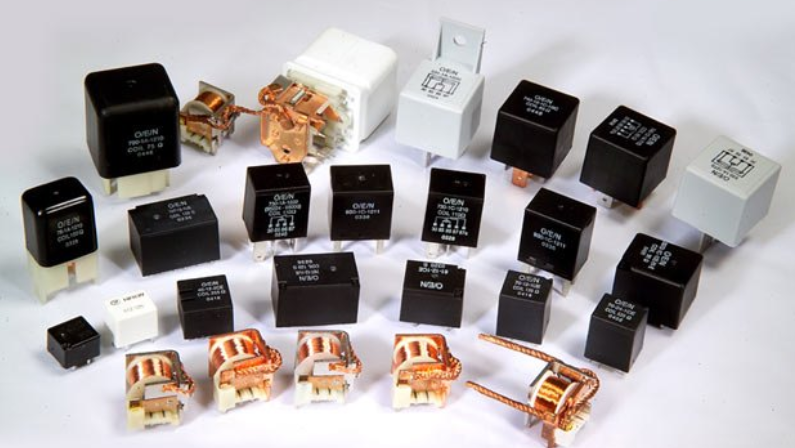

Types of Automotive Relays
Automotive relays come in different types, each designed for specific functions in your vehicle’s electrical system. Understanding the types can help you know how they work and where they’re used.
Here are some of the most common ones:
1. By Switching Type
Relays can be grouped based on how they control the flow of current. Here are the most common switching types:
- Change-Over Relay: Switches between two circuits, allowing one to turn off while the other turns on.
- Normally Open Relay (NO): The default state keeps the main circuit off. It activates and closes the circuit when the coil is energized.
These types are used to control various functions like headlights, fuel pumps, and fans, helping manage electrical loads safely and efficiently.
2. By Function
Automotive relays can also be grouped by the specific function they perform in the vehicle. Here are the most common types:
- Make and Break Relay: Turns a circuit on or off, allowing or stopping the flow of electricity.
- Time-Delay Relays: Delays the switch-on or switch-off of a circuit, often used in interior lights or defrosters.
- Flasher Relay: Used in turn signals and hazard lights to create the blinking effect.
- Electromagnetic Relays: Use an electromagnet to open or close circuits; these are the traditional types found in many car systems.
- Solid-State Relays: Have no moving parts and rely on electronic components; they’re more durable and faster than electromagnetic types.
- Protective Relays: Monitor current or voltage and shut down circuits when they detect faults, helping prevent damage to electrical systems.
Each type plays a specific role in keeping your car's electronics working smoothly and safely.
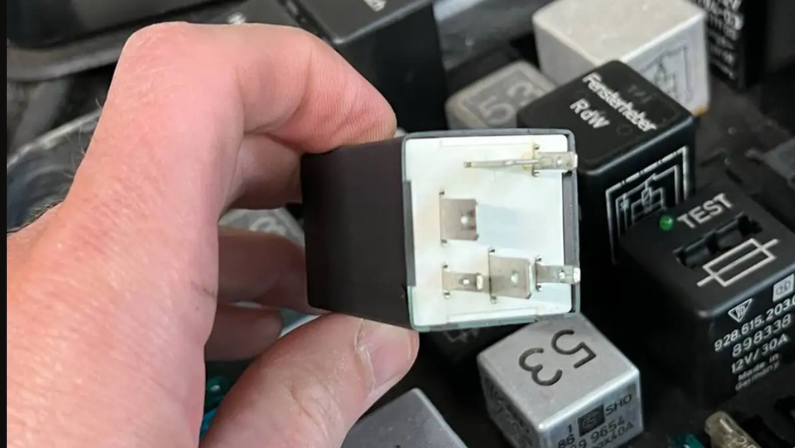
3. By Appearance
Automotive relays also come in different pin configurations, which determine how they connect to circuits. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- 3-Pin Relay: Has three terminals: 30, 86, and 87. It provides a basic on/off control for simple circuits.
- 4-Pin Relay: Commonly used for single-load circuits like fog lamps or horns. Terminals 85 and 86 control the coil, while 30 and 87 handle power flow.
- 5-Pin Relay: Includes an extra terminal, 87a, which allows it to switch between two outputs. Useful for dual-function systems like headlights or brake lights.
- 8-Pin Relay: Can control two different outputs at once from a single switch. It’s more complex and less commonly used in standard vehicles.
Each relay type is suited for specific applications, depending on the complexity of the electrical system.

How Do Car Relays Work?
Automotive relays are switches that use electricity to turn other circuits on or off. Instead of handling high power directly, a small electrical signal from a switch, computer, or control module activates the relay. This lets the relay control bigger electrical currents safely and easily.
Relays help manage power by automating when circuits turn on and off. They can also control multiple circuits at once, even if those circuits use different voltages. This makes your car’s electrical system more efficient and reliable.

Functions of Car Relays
Car relays serve several important functions that help keep your vehicle’s electrical system running smoothly:
1. Protecting Switches
Relays reduce the electrical load on dashboard switches by handling high currents themselves. This prevents switches from overheating or wearing out quickly.
2. Powering Car Lights
Relays allow powerful circuits to control headlights, fog lights, and brake lights. They ensure these lights get enough power without overloading smaller control components.
3. Minimizing Resistance
By using relays placed close to high-power devices, cars reduce the length of heavy wiring. This lowers electrical resistance and prevents voltage drops, improving overall system efficiency.
4. Operating Cooling Fans
Relays control cooling fans for the engine and radiator, turning them on or off as needed to maintain proper temperatures and prevent overheating.
5. Managing Fuel Pumps
Relays control the power supply to the fuel pump, ensuring it runs only when needed. This helps maintain proper fuel pressure and improves engine efficiency and safety by preventing the pump from running continuously.
6. Controlling the Starter Motor
When you turn the ignition key, a relay sends a high current to the starter motor, allowing the engine to crank. This relay protects the ignition switch from handling heavy currents directly, extending its lifespan.
7. Car Locking Mechanism
Relays manage the power for automatic door locks, enabling you to lock or unlock all doors with a push of a button. This system ensures quick and reliable operation of the central locking system.
8. Control the Electrical Magnet
Some relays operate electrical magnets used in various parts of the vehicle, like the starter solenoid. They activate these magnets with a small current to switch larger currents safely and efficiently.

Common Problems with Automotive Relays
Automotive relays can sometimes run into issues that affect how well your car’s electrical systems work. Here are some common problems to watch out for:
1. Sticking Relay
A sticking relay happens when the internal switch gets stuck in the “on” position. This can cause a device like headlights or the fuel pump to stay on even when it shouldn’t, draining the battery or causing damage.
2. Overheating
Relays can overheat if they handle more current than they’re designed for or if there’s a poor connection. Overheating can damage the relay and other parts of the electrical system, leading to failure.
3. Coil Failure
The coil inside the relay creates the magnetic field needed to switch circuits. If the coil burns out or breaks, the relay won’t activate, causing the connected system to stop working.
4. Corrosion
Moisture and dirt can cause corrosion on relay terminals or contacts. Corrosion interferes with electrical flow, leading to unreliable operation or complete failure of the relay.
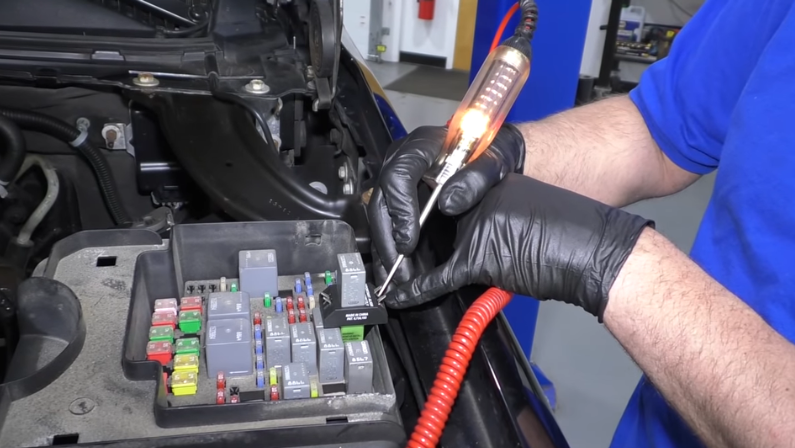

Common Relay Issues: Symptoms, Causes & Fixes
Even reliable relays can fail over time. Here’s how to spot trouble before it leaves you stranded:
1. The Clicking Relay (Most Common Failure)
When your relay sounds like a metronome, but nothing powers on.
Symptoms:
- Rapid clicking sounds when activating components
- Intermittent operation (works sometimes, not others)
Cause:
- Worn-out contacts from repeated use
- Moisture corrosion in the relay housing
Fix:
- Replace with OEM-grade relay ($15-$40)
- Apply dielectric grease to new relay terminals
2. The Silent Relay (Complete Failure)
When your relay gives no response, not even a click.
Symptoms:
- Electrical components are completely dead
- No audible engagement sound
Cause:
- Burnt-out coil from voltage spikes
- Broken solder joints inside the relay
Fix:
- Test by swapping with an identical relay (e.g., borrow a horn relay for testing)
- Check the fuse before replacement
3. The Sticky Relay (Stuck Closed/Open)
When your relay gets "locked" in position.
Symptoms:
- The battery drains overnight
- Components stay on when they shouldn't
- Burning smell near the fuse box
Cause:
- Contacts welded together from high current
- Internal spring failure
Fix:
- Emergency replacement required
- Upgrade to a heavy-duty relay if recurrent issue
4. The Weak Relay (Voltage Drop Issues)
When your relay works... but barely.
Symptoms:
- Headlights dim when using other accessories
- Slow power window operation
Cause:
- Carbon buildup on contacts
- Weak electromagnet coil
Fix:
- Test voltage drop (should be <0.2V across contacts)
- Replace with a low-resistance relay

When to Visit CarHub North York Chrysler’s Service Center
While some relay issues are DIY-friendly, seek professional help if you notice:
- Burning smells or melted plastic near relays
- Multiple electrical failures at once
- Repeated relay failures (indicate deeper wiring problems)
Our technicians can:
- Perform load testing to identify weak relays
- Diagnose hidden wiring faults causing relay stress
- Recommend heavy-duty replacements for high-demand systems

Keep Your Electrical System Running Smoothly
Relays may be small, but their role in your vehicle is massive. When these components fail, they can leave you with mystifying electrical gremlins—from dead headlights to silent horns.
Now that you understand how relays work and why they’re critical, you’ll be better prepared to:
- Diagnose common relay issues (like that telltale clicking sound)
- Spot early warning signs of electrical problems
- Keep all systems running reliably
Need help with car electrical issues? At CarHub North York Chrysler, our technicians use professional diagnostic tools to:
- Test the relay function in minutes
- Pinpoint wiring problems accurately
- Get your vehicle back to 100% operation
Schedule an electrical system check today or visit our service center for expert care. Don’t let a $20 relay leave you stranded!
